- AQH Weekly Deep Dive
- Posts
- Risk Management - Trading Volatile Markets
Risk Management - Trading Volatile Markets
AlgoQuantHub Weekly Deep Dive

Welcome to the Deep Dive!
Here each week on ‘The Deep Dive’ we take a close look at cutting-edge topics on algo trading and quant research.
Last week, we explored the current gold rush and investment opportunities through physical gold purchases and ETC trading. This week, we shift focus from investment opportunities to risk management, exploring how professionals structure portfolios to capture upside while safeguarding against catastrophic drawdowns.
Bonus content: we get tactical, showing how the collar strategy can serve as a mechanical hedge—locking in profits, limiting losses, allowing you to participate in a market or asset rally without fear of being wiped out. By the end of this issue, you’ll have both the philosophy and the tools to approach any volatile asset with a professional, disciplined mindset.
Table of Contents
Exclusive Algo Quant Store & Discounts
Algo Trading & Quant Research Hub
Get 25% off all purchases at the Algo Quant Store with code 3NBN75MFEA
Feature Article: How Pros Manage Risk - A Framework for Profit and Survival
Professionals know that trading is less about predicting markets and more about surviving them. The difference between luck and skill isn’t in how much you make—it’s in how well you protect what you already have.
Markets reward aggression in the short term, but they crown discipline in the long run. Risk management isn’t a checklist to avoid loss; it’s a framework for longevity. The pros don’t see hedging as a cost—they see it as the price of staying in the game. Similarly modern traders don’t just monitor markets; they encode their risk logic into algorithms, ensuring every trade executes according to rules rather than emotion.
A robust risk framework has three moving parts:
1. Define Exposure. Know precisely what you’re betting on—direction, volatility, or correlation—and size positions so no single view can ruin you.
2. Design Boundaries. Every trade needs built-in limits: stop-loss levels, profit targets, and conditional hedges such as collars or volatility-based position reductions.
3. Automate Execution. Once your parameters are clear, code them. Let your system rebalance, hedge, and scale exposure automatically so decisions happen without panic or hesitation.
Let’s use the current gold rally as a live example. Gold prices recently breached an all-time high of $4,000 per troy ounce, driven by macroeconomic uncertainty and strong investor demand. It’s a textbook case of exuberance meeting momentum. The temptation is to stay long and ride the wave—but a professional asks: what if I’m wrong? Volatility has been creeping lower even as prices rise (the leverage effect), meaning the market is probably underpricing risk. This makes now an ideal time to hedge: lower implied volatility means cheaper downside protection.
This asymmetry—where fear is low but danger is high—is where smart hedgers quietly lock in survival. By capping risk when others are relaxed, they protect capital before storms hit.
Your risk management framework should therefore be dynamic—automatically scaling protection as volatility compresses and relaxing it as volatility spikes. Once that rhythm is coded into your system, hedging becomes an algorithmic reflex rather than a human reaction. You no longer trade markets manually; you engineer exposure through automation, transforming risk control into part of the trading architecture itself.
Further Reading:
Keywords
risk management, trading strategies, trading, position sizing, volatility, hedging, survival , risk framework, algorithmic, financial risk, portfolio engineering, market momentum trading, gold rally, implied volatility, downside protection, market risk, trading discipline, trading psychology, risk-adjusted returns
Advert: Algorithmica - The Ultimate Quant Analytics & Risk Management Platform
Algorithmica leads the world in real-time, cross-asset quantitative analytics and risk management. Its flagship Quantlab platform delivers unparalleled speed and flexibility for quants, traders, and analysts—providing seamless integration of real-time market data, historical time series, and financial modelling all in one agile system.
Paired with ARMS, our cutting-edge risk management system, Algorithmica empowers front offices to control market, counterparty, and liquidity risk in real time with transformational performance and deep portfolio insights.
Trusted for its robust, agile solutions and rapid deployment—Algorithmica is the choice for forward-looking financial institutions worldwide seeking a competitive edge. Elevate your quantitative analytics and risk framework with the best in the business.
Click-here to contact us and experience the power of Algorithmica.
Keywords:
World Class, Trading Software, Quantitative Analytics, Risk Management, Financial Data
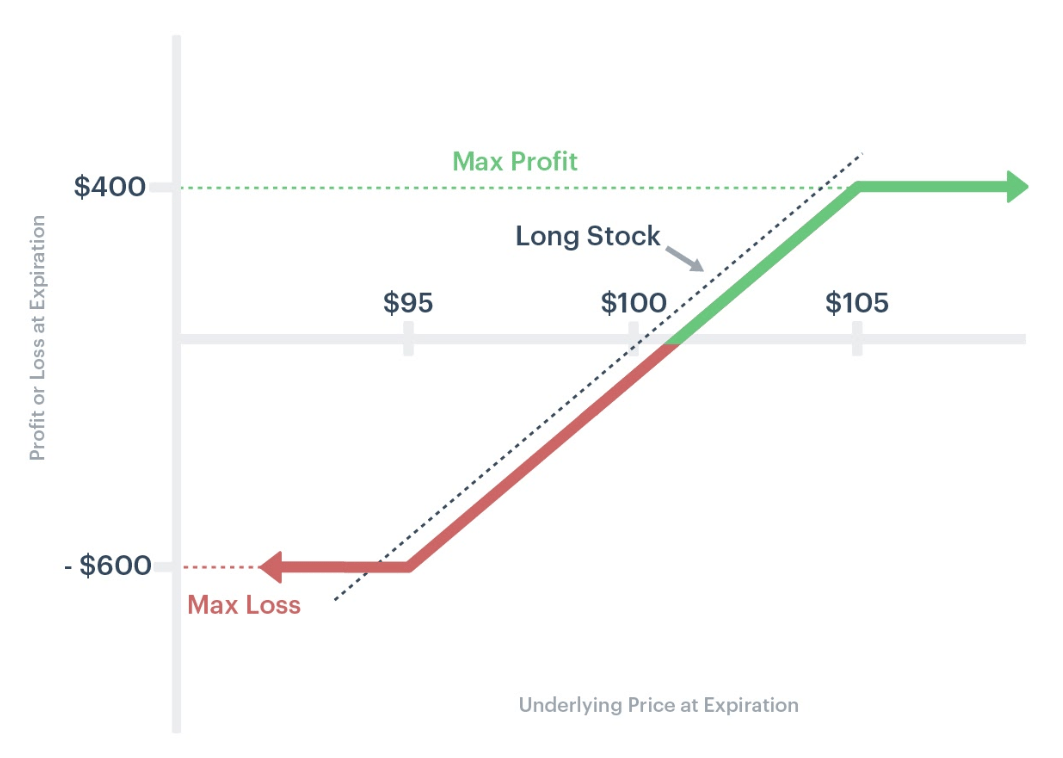
Bonus Content: The Collar Strategy – Designing Boundaries for Profit and Protection
A collar is one of the simplest and most elegant ways to turn an uncertain position into a defined one—a safety net with profit targets built in.
In essence, a collar combines the ownership of the underlying asset (like gold, mining equities, or ETFs) with a long put and a short call. The long put guarantees a minimum sale price—your disaster insurance—while the short call caps your profit at a chosen level, often funding the cost of the put. Together, they transform randomness into structure.
If you already hold the underlying, you can build a collar by adding a risk reversal (short call, long put). Think of it as engineering both a stop loss and a take profit directly into your portfolio. Once the call is exercised, you exit profitably; if the put triggers, you’re stopped out in a controlled way. Either way, you’ve locked in a range of outcomes—profit or protection, never ruin.
In the current gold rally, this strategy is particularly compelling. Volatility is lower during the uptrend, which makes puts cheaper and allows traders to hedge at a discount. This is related to what quants call the leverage effect—as prices rise, implied volatility tends to fall, and vice versa. So now is the time to build protection while the market is relaxed.
To design the collar effectively, choose your target profit and stop-loss levels based on meaningful market structure, not short-term noise. You want strikes wide enough to absorb normal retracements but close enough to preserve value if the bubble bursts. For example, setting your put roughly 10–15% below current price and the call 5–10% above gives you an asymmetric, cost-neutral hedge that works even in volatile bursts.
For long-term investors like pension funds or physical gold holders, the logic changes slightly. You’re not hedging every price move—you’re guarding against catastrophic tail risk. Here, futures or index options may serve as proxy hedges, protecting portfolio value without directly selling the physical or core holdings. For traders, however, the collar provides a hands-on, adaptive tool that can be renewed periodically as the market evolves.
Over time, this approach can be repeated cyclically: if the short call is exercised, you sell into strength, re-establish your long position, and set up a new collar. If the put triggers, you exit gracefully and wait for re-entry at fairer valuations. It’s an elegantly simple loop of discipline through design—transforming trading from intuition into engineered execution.
Keywords:
Trading, Hedging, Risk Management, Stop-Loss, Take Profit, Bracket Orders, Guaranteed Stop-Loss, Collar Trading Strategy, Long Position with Risk Reversal
Training Resources: Live Options Trading, Pricing & Risk
Take your understanding from theory to practice with our YouTube training series and premium Excel workbooks. These hands-on resources walk you through live option pricing, risk management, and trading strategies used by professional traders. Each model is built for real-market application, helping you visualise payoff structures, Greeks, and risk-reward dynamics in real time. Whether you’re refining your quant skills or developing your own automated trading system, these materials give you the edge to trade options with confidence and precision.
Useful Links
Quant Research
SSRN Research Papers - https://ssrn.com/author=1728976
GitHub Quant Research - https://github.com/nburgessx/QuantResearch
Learn about Financial Markets
Subscribe to my Quant YouTube Channel - https://youtube.com/@AlgoQuantHub
Quant Training & Software - https://payhip.com/AlgoQuantHub
Follow me on Linked-In - https://www.linkedin.com/in/nburgessx/
Explore my Quant Website - https://nicholasburgess.co.uk/
My Quant Book, Low Latency IR Markets - https://github.com/nburgessx/SwapsBook
AlgoQuantHub Newsletters
The Edge
The ‘AQH Weekly Edge’ newsletter for cutting edge algo trading and quant research.
https://bit.ly/AlgoQuantHubEdge
The Deep Dive
Dive deeper into the world of algo trading and quant research with a focus on getting things done for real, includes video content, digital downloads, courses and more.
https://bit.ly/AlgoQuantHubDeepDive
Feedback & Requests
I’d love your feedback to help shape future content to best serve your needs. You can reach me at [email protected]