- AQH Weekly Deep Dive
- Posts
- Quant Models - How to Calibrate Yield Curves & Credit Curves?
Quant Models - How to Calibrate Yield Curves & Credit Curves?
AlgoQuantHub Weekly Deep Dive

Welcome to the Deep Dive!
Here each week on ‘The Deep Dive’ we take a close look at cutting-edge topics on algo trading and quant research.
This Week, we dive into the essential mechanics of yield curve calibration and discover how forward rates and discount factors are extracted from swap prices and drive the pricing of interest rate products and present value calculations.
Bonus Content, explore credit curve calibration and learn how from CDS prices we can imply hazard rates (default intensities) and default probabilities for pricing bonds and credit-risky instruments.
Table of Contents
Feature Article: Yield Curve Calibration
How to Imply Froward Rates and Discount Factors from Swap Prices?
Yield curve calibration is the process of recovering market data from the prices of liquid instruments. In interest rate markets, we start by observing the market prices of liquid instruments: interest rate swaps, futures and cash deposits—and we treat these prices as model inputs. The yield curve model then solves for the forward rates and discount factors required to price these market instruments exactly. This is our model output.
Yield curve models assume forward interest rates follow a smooth functional form or curve. Many production-grade systems represent forward rates as a cubic spline and solve for the spline parameters. This is done in such a way that the resulting forward rate curve reproduces observed market prices exactly.
This is not aesthetic curve-fitting; it is a constrained, no-arbitrage calibration problem. Once solved, the result is a forward-rate curve that can be used to price any instrument that depends on those forwards, not just the calibration instruments themselves.
Crucially, this calibrated forward interest rate curve can also be used to imply discount factors required for present-value calculations. This makes yield curve calibration tantamount to pricing itself, since almost all financial instruments are required to discount their cashflows. This market data forms the backbone of valuation for many rates products, from swaps and FRAs to caps, floors, exotics, and structured rates products.
Interest Rate Markets Training Guide
For a comprehensive training guide on interest rate markets, written by a market practitioner and presented at Imperial College Business School, download the free primer here.
YouTube: Yield Curve Training
Yield curve calibration is explained step-by-step in my YouTube walkthrough.
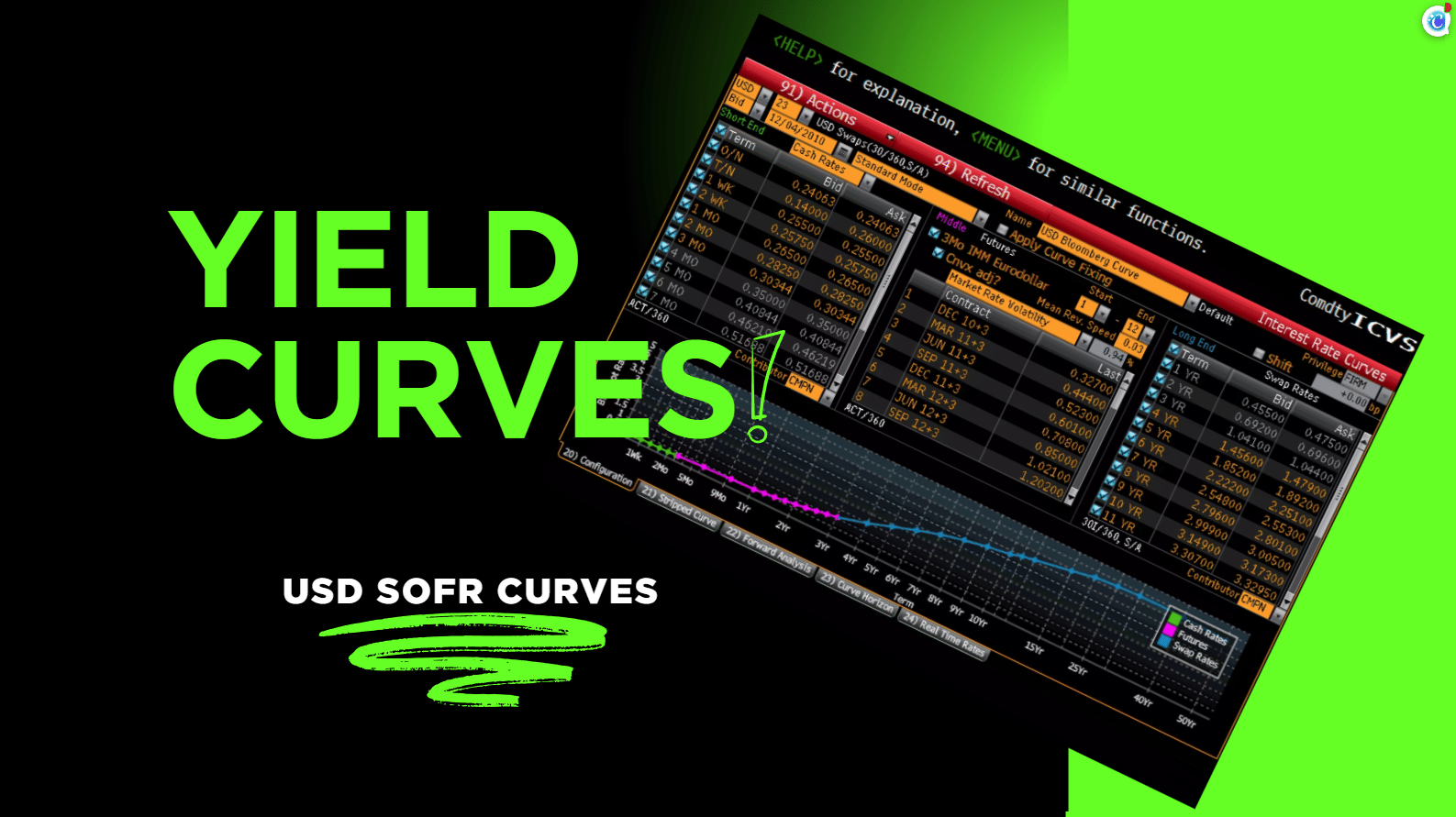
Yield Curve Training Software
For a desk-ready demo yield curve in Excel see AlgoQuantHub, where we calibrate a USD SOFR yield curve directly to interest rate swap par rates and demo how the yield curve model generates the forward rates and discount factors that exactly reprice these swaps as output.
USD SOFR Yield Curve Calibration
An Excel workbook with video training to demonstrate how to:
Calibrate a USD SOFR yield curve from market swap quotes
Generate forward rates and discount factors for pricing
Price interest rate swaps directly from your curve
Compute and interpret swap risk metrics using the curve’s Jacobian—essential for real-time risk and model sensitivity analysis
Excel Workbook: https://payhip.com/b/PCNBk
Keywords:
yield curve, calibration, forward rates, discount factors, interest rate swaps, cubic spline, SOFR, curve construction, quantitative finance
Bonus Article: Credit Curve Calibration
While yield curves describe the time value of money, credit curves describe the probability of not receiving it. A credit curve is calibrated to CDS prices (par spreads) and requires discount factor market data as an input—typically sourced from the relevant OIS or risk-free yield curve. The calibration process solves for a term structure of hazard rates (default intensities), which encode the market-implied probability of default across maturities. These hazard rates are essential for pricing bonds, CDS, and any credit-sensitive instrument where counterparty default is a material risk. In modern markets, credit curve calibration is the mechanism that translates observable CDS prices into implied default probabilities used across credit trading, risk management, and valuation.
Credit Curve Training Software
For a demo credit curve in Excel see AlgoQuantHub, where we calibrate a USD Treasury curve to credit default swap (CDS) par spreads and demo how the credit curve model generates the hazard rates (default intensities) and default probabilities needed to reprice such market CDS instruments exactly.
Credit Model Calibration
An Excel workbook to demonstrate how to calibrate a credit curve. It includes:
Credit curve calibration using market CDS inputs.
Full pricing and repricing of CDS calibration instruments
Full implementation of multivariate Newton-Raphson Algorithm
Analytical and numerical computation of the Jacobian matrix
Bespoke CDS pricing using the hazard rates i.e. curve calibration outputs
Excel Workbook: https://payhip.com/b/9mTtc
Keywords:
credit curve, calibration, CDS pricing, hazard rates, probability of default, credit risk, quantitative credit, bond pricing
Exclusive Algo Quant Store Discounts
Algo Trading & Quant Research Hub
Get 25% off all purchases at the Algo Quant Store with code 3NBN75MFEA.
Useful Links
Quant Research
SSRN Research Papers - https://ssrn.com/author=1728976
GitHub Quant Research - https://github.com/nburgessx/QuantResearch
Learn about Financial Markets
Subscribe to my Quant YouTube Channel - https://youtube.com/@AlgoQuantHub
Quant Training & Software - https://payhip.com/AlgoQuantHub
Follow me on Linked-In - https://www.linkedin.com/in/nburgessx/
Explore my Quant Website - https://nicholasburgess.co.uk/
My Quant Book, Low Latency IR Markets - https://github.com/nburgessx/SwapsBook
AlgoQuantHub Newsletters
The Edge
The ‘AQH Weekly Edge’ newsletter for cutting edge algo trading and quant research.
https://bit.ly/AlgoQuantHubEdge
The Deep Dive
Dive deeper into the world of algo trading and quant research with a focus on getting things done for real, includes video content, digital downloads, courses and more.
https://bit.ly/AlgoQuantHubDeepDive
Feedback & Requests
I’d love your feedback to help shape future content to best serve your needs. You can reach me at [email protected]