- AQH Weekly Deep Dive
- Posts
- Machine Learning for Algorithmic Trading & PCA for Statistical Arbitrage
Machine Learning for Algorithmic Trading & PCA for Statistical Arbitrage
AlgoQuantHub Weekly Deep Dive

Welcome to the Deep Dive!
Here each week on ‘The Deep Dive’ we take a close look at cutting-edge topics on algo trading and quant research.
Last week, we explored the world of stablecoins — the “digital dollars” reshaping crypto markets, payments, and even global finance, from how they work to where the real opportunities (and risks) lie. This week, we demystify some of the core machine learning methods used for algo trading with examples in python.
Bonus content, this week we outline the use principal component analysis (PCA) for trading strategies such as statistical arbitrage.
Table of Contents
Exclusive Algo Quant Store & Discounts
Get 25% off all purchases at the Algo Quant Store with code 3NBN75MFEA
Feature Article: How Machine Learning Can Transform Your Algo Trading Strategies
Machine learning is rapidly reshaping modern trading. Beyond traditional models, ML uncovers subtle market signals, adapts to shifting conditions, and unlocks strategies once out of reach. In this article, we’ll cut through the hype and show how ML can drive real impact in your algo trading. From understanding the layers of AI, to applying core ML techniques for markets, we’ll walk through practical examples—predicting market direction, enhancing pairs trading with PCA, and pushing the frontier with reinforcement learning for strategy optimisation. If you’re ready to see how ML can give your trading strategies an edge, let’s dive in.
1. Layers of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a broad field focused on building systems that mimic human intelligence. Within AI, Machine Learning (ML) consists of algorithms learning patterns from data rather than explicit programming. Nested deeper, Deep Learning (DL) uses multi-layered neural networks to uncover complex, non-linear data relationships. At the cutting edge, Generative AI goes further, creating new content such as trading signals or text. Together these AI layers empower advanced financial technology and algorithmic trading.
2. Core ML Methods for Trading
Common ML techniques used in algo trading include:
KNN (K-Nearest Neighbours): Classifies signals by similarity in historical data.
K-Means Clustering: Identifies distinct market regimes or clusters.
Naïve Bayes Classification (NBC): Employs probabilistic models, useful in market sentiment classification.
Support Vector Machines (SVM): Best for trend and regime classification with maximal margin.
Self-Organising Maps (SOM): For dimensionality reduction and market visualization.
Decision Trees & Random Forests: Effective for feature importance and regime detection.
Neural Networks (NNs): Capture non-linearity in market data.
Reinforcement Learning (RL): Learns sequential trading decisions optimizing cumulative reward
3. Example – Predicting Market Direction
A classic example is predicting short-term market direction. Features like returns, volatility, technical indicators, and order book data can be inputs to SVM or Random Forests models to classify the next step's direction (up/down). A trading signal is generated when the predicted probability of an up move surpasses a threshold, filtering noise and enhancing entry timing. This approach yields a systematic method to capitalize on persistent patterns.
Instead of guessing price moves, you can frame it as a classification problem: will the next period be up or down? Features like recent returns, volatility, and technical indicators feed into models like SVM or Random Forests. A buy signal is triggered when the model predicts “up” with high confidence.
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Example features: returns & rolling volatility
df["return"] = df["Close"].pct_change()
df["volatility"] = df["return"].rolling(10).std()
df["direction"] = (df["return"].shift(-1) > 0).astype(int) # target
X = df[["return", "volatility"]].dropna()
y = df["direction"].dropna()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, shuffle=False)
model = RandomForestClassifier().fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predict next step's direction
signal = model.predict_proba(X_test.tail(1))[:,1] > 0.55
print("Buy" if signal else "Sell")
Pro Tip:
Combine diverse feature sets like volume, order flow, and regime indicators, and use probabilistic thresholds dynamically adjusted by recent model performance to improve reliability.
4. Example – Pairs Trading Using PCA
Aside from individual asset prediction, pairs trading exploits mean-reversion between correlated asset pairs. Recent advances use Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to identify pairs by decomposing price returns into orthogonal components. By selecting pairs corresponding to the highest and lowest absolute loadings in the first principal component, traders find cointegrated assets with stable long-term relationships. Signals are generated using spread stationarity and mean reversion metrics, allowing market-neutral profit opportunities independent of broader trends.
Pairs trading looks for mean-reverting spreads between correlated assets. PCA helps by finding hidden factors across many assets and identifying pairs most sensitive to the same factor. You can then trade their spread when it deviates too far from the mean.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
# Assume df = prices of multiple stocks
returns = df.pct_change().dropna()
pca = PCA(n_components=1).fit(returns)
loadings = pca.components_[0]
# Pick two assets with extreme loadings
i, j = np.argsort(loadings)[[0, -1]]
pair = (df.columns[i], df.columns[j])
spread = df[pair[0]] - df[pair[1]]
zscore = (spread - spread.mean())/spread.std()
# Trading rule
if zscore.iloc[-1] > 2:
print("Short spread (short A, long B)")
elif zscore.iloc[-1] < -2:
print("Long spread (long A, short B)")
Pro Tip:
Use rolling PCA and continuously update pair selections and thresholds; combine with econometric cointegration testing and factor adjustments to maintain robustness in live markets.
Reinforcement Learning learns trading policies: when to buy, sell, or hold to maximize long-term reward. Unlike static models, the agent adapts as market conditions shift.
5. Reinforcement Learning for Strategy Optimisation
Reinforcement Learning optimizes trading by learning policies that maximize cumulative returns rather than single-step predictions. Agents learn actions such as entry, exit, or hold positions in simulated environments accounting for costs and risks. Techniques like Q-learning and Deep Q-Networks enable adaptive strategies evolving with the changing market landscape.
Reinforcement Learning learns trading policies: when to buy, sell, or hold to maximize long-term reward. Unlike static models, the agent adapts as market conditions shift.
import gym
import numpy as np
import gym_anytrading # pip install gym-anytrading
env = gym.make("stocks-v0", frame_bound=(50, 200), window_size=10)
state = env.reset()
# Simple Q-learning loop (toy example)
q_table = {}
alpha, gamma, epsilon = 0.1, 0.99, 0.1
for _ in range(500):
state = env.reset()
done = False
while not done:
action = env.action_space.sample() if np.random.rand() < epsilon else 0
new_state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
q_table[state] = q_table.get(state, [0,0])
q_table[state][action] = (1-alpha)*q_table[state][action] + \
alpha*(reward + gamma*max(q_table.get(new_state,[0,0])))
state = new_state
Pro Tip:
Incorporate realistic transaction costs and risk constraints directly into the reward function and leverage transfer learning from multiple market regimes for better generalization.
Recommended Resources:
Best Software for Algo Trading
Layers of AI - What is driving advancements in generative AI?
Machine Earning - Algo Trading Strategies
Machine Learning - An Applied Mathematics Introduction
Machine Learning in Trading - Step by Step Implementation
Top 10 Algo Trading Strategies
Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Generative AI, Algorithms, Algo Trading, Machine Learning Methods, Kth Nearest Neighbours, K-Means Clustering, Support Vector Machines, Neural Networks, Reinforcement Learning, Trading Strategies
Bonus Content: PCA for Statistical Arbitrage - Step-by-Step in Python
In this week’s bonus section, we go hands-on with an end-to-end Python Jupyter Notebook that demonstrates how Principal Component Analysis (PCA) can be leveraged in algorithmic trading strategies.
Python Jupyter Notebook
In the corresponding Python Jupyter Notebook click-here, we provide a step-by-step build, starting from core mathematical intuition and working all the way up to trading signal ideas. Along the way, you’ll see exactly how PCA captures hidden factors, reduces noise, and extracts actionable insights from market data. Here’s what the notebook covers in depth,
Building PCA from First Principles
How to download price data, compute returns, construct covariance matrices.
Calculate eigenvalues & eigenvectors directly via
numpy.linalg.Understand the mathematical foundation of PCA rather than relying on black-box libraries.
Visualization and Intuition
Plot prices, log returns, and PCA eigenvectors to reveal hidden structure.
Compare PCA mechanics with OLS regression, clarifying why PCA captures true underlying factors across multiple assets.
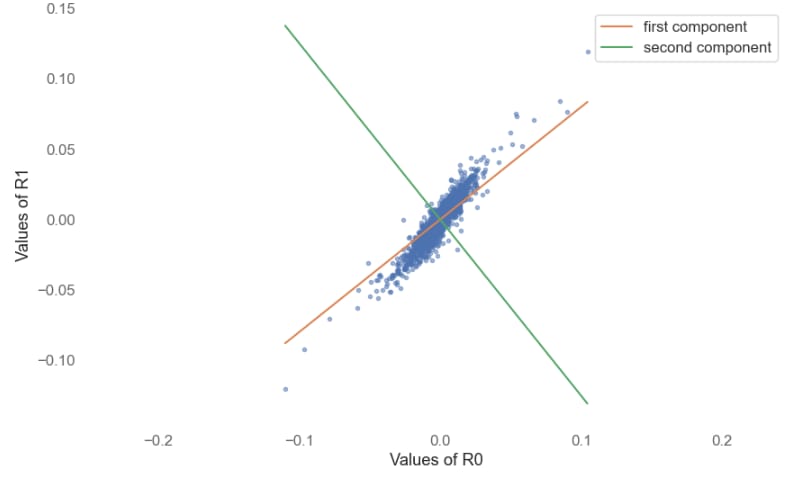
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) - Plot of First Two Components
Portfolio Applications of PCA
Construct an eigenportfolio ordered by significance
Use explained variance ratios to decide how many factors to use
Apply PCA clustering to identify similar stocks for pairs trading, hidden factors, or co-movement patterns.

Plot of Stock Returns First Two Principal Components
Commodities (Red), Technology Stocks (Blue) and Banking Stocks (Green)
Turning PCA into Trading Signals
Compare market prices with PCA-implied prices.
Test for cointegration (Engel-Granger tests, causality direction).
Identify sector-driven arbitrage relationships (e.g., crude oil leading gasoline).
Build a statistical arbitrage strategy that trades residual spreads between an index (e.g. S&P500) and its PCA-based replication portfolio.
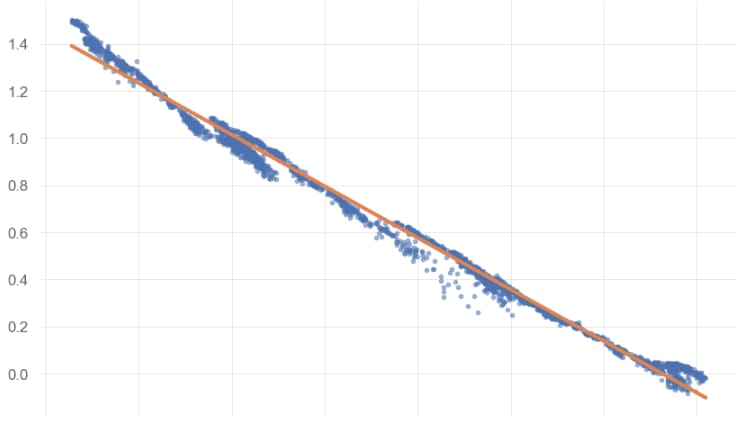
Plot of Eigen-Portfolio and the SPY ETF
Trading Strategy Implementation
Compare market prices with PCA implied prices and track the spread
Detect trading opportunities when spreads deviate beyond a threshold.
Enter mean-reversion trades (long/short residual).
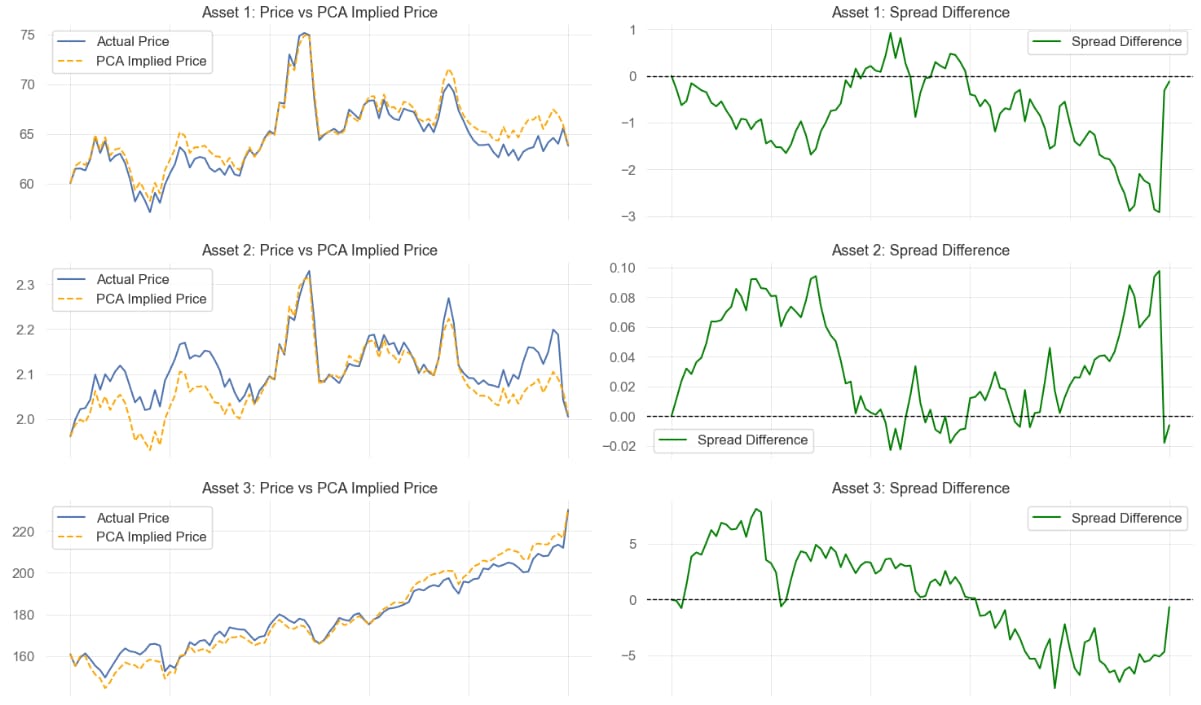
Stock Price vs PCA Implied Price - Spread can be used to Generate Trading Signals
🚀 Why This Matters for Quant Traders
PCA is far more than an academic exercise — in trading it provides tools to:
Detect hidden risk factors driving correlated assets.
Cluster assets to diversify portfolios.
Find pairs for statistical-arbitrage through cointegration checks.
Replicate indices and exploit spreads for arbitrage.
Build factor-based ML models with cleaner, noise-reduced features.
By the end of the notebook, you’ll have both the theoretical intuition and the fully coded implementation of PCA-based trading ideas — ready to be integrated, modified, and extended into production strategies.
This is the kind of applied machine learning tutorial that transforms textbook math into market alpha.
Keywords
Principal Component Analysis, PCA, Statistical Arbitrage, Pairs Trading, Trading Strategies, Asset Clustering, Risk Factors, Factor-Based Models, Machine Learning, Index Replication, Cointegration, Covariance
Useful Links
Quant Research
SSRN Research Papers - https://ssrn.com/author=1728976
GitHub Quant Research - https://github.com/nburgessx/QuantResearch
Learn about Financial Markets
Subscribe to my Quant YouTube Channel - https://youtube.com/@AlgoQuantHub
Quant Training & Software - https://payhip.com/AlgoQuantHub
Follow me on Linked-In - https://www.linkedin.com/in/nburgessx/
Explore my Quant Website - https://nicholasburgess.co.uk/
My Quant Book, Low Latency IR Markets - https://github.com/nburgessx/SwapsBook
AlgoQuantHub Newsletters
The Edge
The ‘AQH Weekly Edge’ newsletter for cutting edge algo trading and quant research.
https://bit.ly/AlgoQuantHubEdge
The Deep Dive
Dive deeper into the world of algo trading and quant research with a focus on getting things done for real, includes video content, digital downloads, courses and more.
https://bit.ly/AlgoQuantHubDeepDive
Feedback & Requests
I’d love your feedback to help shape future content to best serve your needs. You can reach me at [email protected]